Оштрафованный порог для вейвлета 1D или 2D шумоподавление
THR = wbmpen(C,L,SIGMA,ALPHA)
wbmpen(C,L,SIGMA,ALPHA,ARG)
THR = wbmpen(C,L,SIGMA,ALPHA) возвращает глобальный порог THR для шумоподавления. THR получен содействующим правилом выбора вейвлета с помощью метода пенализации, предоставленного Birgé-Massart.
[C,L] является структурой разложения вейвлета сигнала или изображения, чтобы быть denoised.
SIGMA является стандартным отклонением нулевого среднего Гауссова белого шума в модели шумоподавления (см. wnoisest для получения дополнительной информации).
ALPHA является настраивающимся параметром для термина штрафа. Это должно быть вещественное число, больше, чем 1. Разреженность представления вейвлета сигнала denoised или изображения растет с ALPHA. Обычно ALPHA = 2.
THR минимизирует оштрафованный критерий, данный следующим:
Позвольте t* быть минимизатором
crit(t) = -sum(c(k)^2,k≤t) + 2*SIGMA^2*t*(ALPHA + log(n/t))
где c(k) является коэффициентами вейвлета, отсортированными в порядке убывания их абсолютного значения, и n является количеством коэффициентов; затем THR = | c (t*) |.
wbmpen(C,L,SIGMA,ALPHA,ARG) вычисляет глобальный порог и, кроме того, строит три кривые:
2*SIGMA^2*t*(ALPHA + log(n/t))
sum(c(k)^2,k²t)
crit(t)
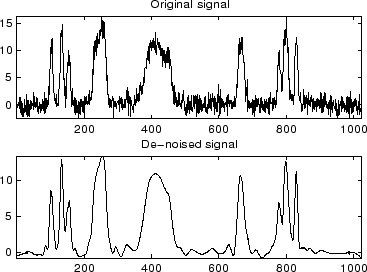
% Example 1: Signal denoising.
% Load noisy bumps signal.
load noisbump; x = noisbump;
% Perform a wavelet decomposition of the signal
% at level 5 using sym6.
wname = 'sym6'; lev = 5;
[c,l] = wavedec(x,lev,wname);
% Estimate the noise standard deviation from the
% detail coefficients at level 1, using wnoisest.
sigma = wnoisest(c,l,1);
% Use wbmpen for selecting global threshold
% for signal denoising, using the tuning parameter.
alpha = 2;
thr = wbmpen(c,l,sigma,alpha)
thr =
2.7681
% Use wdencmp for denoising the signal using the above
% threshold with soft thresholding and approximation kept.
keepapp = 1;
xd = wdencmp('gbl',c,l,wname,lev,thr,'s',keepapp);
% Plot original and denoised signals.
figure(1)
subplot(211), plot(x), title('Original signal')
subplot(212), plot(xd), title('De-noised signal')
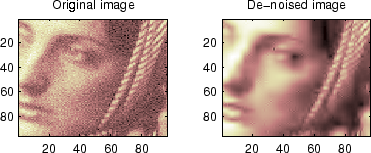
% Example 2: Image denoising.
% Load original image.
load noiswom;
nbc = size(map,1);
% Perform a wavelet decomposition of the image
% at level 3 using coif2.
wname = 'coif2'; lev = 3;
[c,s] = wavedec2(X,lev,wname);
% Estimate the noise standard deviation from the
% detail coefficients at level 1.
det1 = detcoef2('compact',c,s,1);
sigma = median(abs(det1))/0.6745;
% Use wbmpen for selecting global threshold
% for image denoising.
alpha = 1.2;
thr = wbmpen(c,l,sigma,alpha)
thr =
36.0621
% Use wdencmp for denoising the image using the above
% thresholds with soft thresholding and approximation kept.
keepapp = 1;
xd = wdencmp('gbl',c,s,wname,lev,thr,'s',keepapp);
% Plot original and denoised images.
figure(2)
colormap(pink(nbc));
subplot(221), image(wcodemat(X,nbc))
title('Original image')
subplot(222), image(wcodemat(xd,nbc))
title('De-noised image')