By default, the compression-ignition (CI) engine dynamometer reference application engine
is configured with a dynamic 1.5-L turbocharged diesel engine. Based on a desired number of
cylinders and maximum engine power or engine displacement, you can resize the dynamic engine
(CiEngine) for different vehicle applications.
To resize the engine, use the dynamometer reference application. After you open the reference application, click Resize Engine and Recalibrate Controller. In the dialog box, set Power or displacement to either:
Power – Enter a Desired maximum
power value
Displacement – Enter a Desired
displacement value
For either power or displacement, enter a Desired number of cylinders value.
After you apply the changes, the reference application:
Resizes the dynamic engine and engine calibration parameters. The Resize Engine and Recalibrate Controller block mask provides the updated engine performance characteristics based on the resized calibration parameters.
Recalibrates the controller and mapped engine model to match the resized dynamic engine.
You can use the variants in other applications, for example, in vehicle projects that require a larger engine model.
If it is not already open, open a copy of the CI engine reference application project by entering
In the CiDynoReferenceApplication model window, click
Recalibrate Controller.
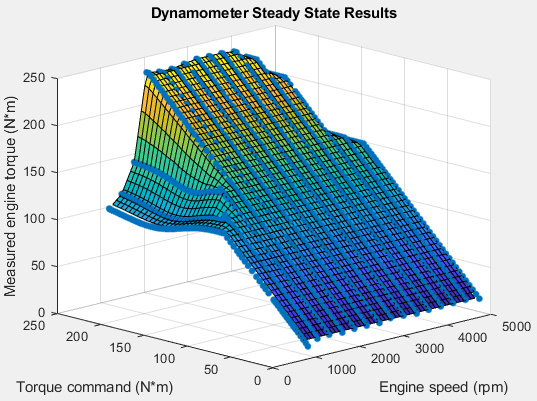
The reference application performs a dynamometer test to calibrate the engine controller for the default 1.5-L turbocharged diesel engine. For engine speeds 2000–5000 rpm, the measured engine torque approaches 240 N·m. The steady-state results for measured engine torque as a function of torque command and engine speed are similar to this plot.
In the CiDynoReferenceApplication model window, click
Resize Engine and Recalibrate Controller.
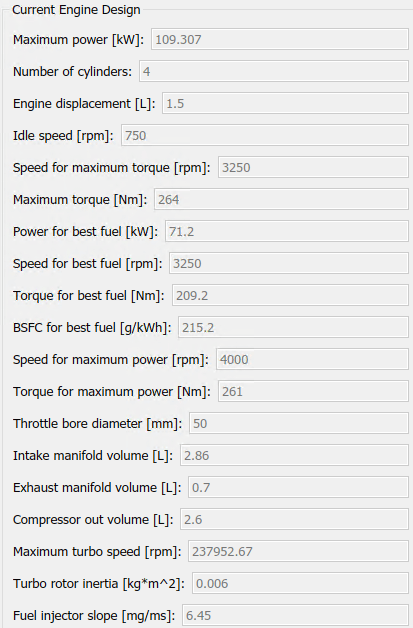
The dialog box opens with default values for Desired maximum power and Desired number of cylinders. These values represent the calibration parameters for the default 1.5-L dynamic engine.
The dialog box provides the calibration parameters for the current engine design. The parameters are similar to these.
In the Resize Engine and Recalibrate Controller dialog box, enter values that represent approximately twice the maximum power and number of cylinders. For example, set:
Desired maximum power to
220.
Desired number of cylinders to
8.
Click Resize Engine. The reference application:
Resizes the dynamic engine (CiEngineCore)
and engine calibration parameters. The dialog box provides the
updated engine performance characteristics based on the resized
calibration parameters.
Recalibrates the controller
(CiEngineController) and mapped engine
model (CiMappedEngine) to match the resized
dynamic engine (CiEngineCore).
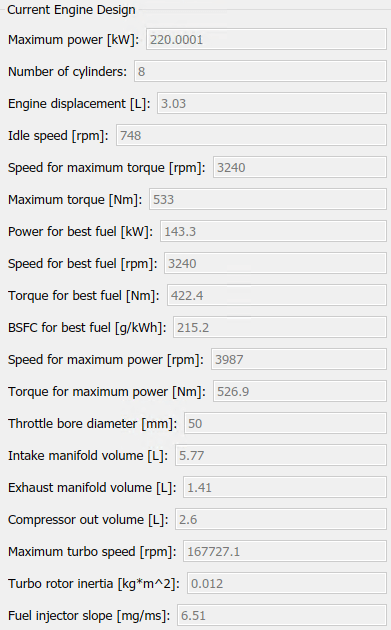
After resizing and recalibration, the dialog box provides the calibration parameters for the resized engine. The parameters are similar to these.
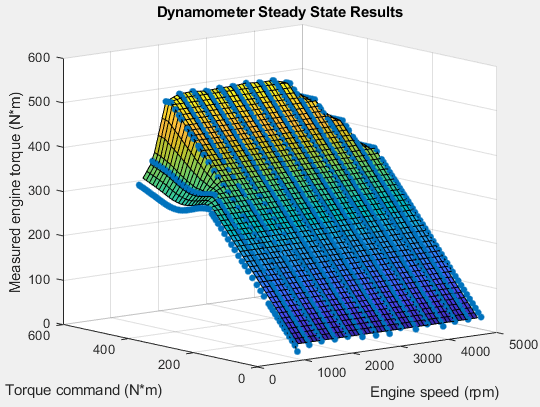
Examine the dynamometer steady-state results. For engine speeds 2000–5000 rpm, the measured engine torque approaches 500 N·m. This result is approximately twice the power of the default dynamic engine. The steady-state results for measured engine torque as a function of torque command and engine speed are similar to this plot.
To save the engine controller, resized engine mapped variant, and resized
dynamic engine variant, in the CiDynoReferenceApplication
model window, save the reference application.
By default, this process creates:
An updated CI engine controller
Two engine variants — mapped and dynamic
To see the parameters associated with the controller and engine variants:
In MATLAB®, use the Project Shortcuts tab to open these models:
CiEngineController
CiEngineCore
CiMappedEngine
Use the Model Explorer to view the resized parameters:
| Engine Model | Model Explorer |
|---|---|
|
Controller —
|
|
|
Mapped — |
|
|
Dynamic — |
|
In the CiDynoReferencApplication > Engine
System > Engine Plant >
Engine > CIMappedEngine subsystem,
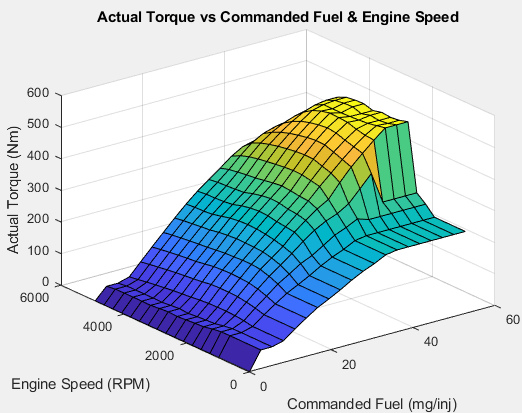
open the Mapped CI Engine block. On the Power tab, plot the
actual torque as a function of engine speed and commanded fuel.
CI Core Engine | Mapped CI Engine